Solved Problems
Part 1
1- In the snail Cepaea nemoralis, an autosomal allele causing a banded shell (BB) is recessive to the allele for an unbanded shell (BO). Genes at a different locus determine the background color of the shell; here, yellow (CY) is recessive to brown (CBw). A banded, yellow snail is crossed with a homozygous brown, unbanded snail. The F1 are then crossed with banded, yellow snails (a testcross).
- What will the results of the testcross be if the loci that control banding and color are linked with no crossing over?
- What will the results of the testcross be if the loci assort independently?
- What will the results of the testcross be if the loci are linked and 20 m.u. apart?
=> (SOLUTION)
2- In silkmoths (Bombyx mori), red eyes (re) and white-banded wing (wb) are encoded by two mutant alleles that are recessive to those that produce wild-type traits (re+ and wb+); these two genes are on the same chromosome. A moth homozygous for red eyes and white-banded wings is crossed with a moth homozygous for the wild-type traits. The F1 have normal eyes and normal wings. The F1 are crossed with moths that have red eyes and white-banded wings in a testcross. The progeny of this testcross are:
wild-type eyes, wild-type wings 418
red eyes, wild-type wings 19
wild-type eyes, white-banded wings 16
red eyes, white-banded wings 426
- What phenotypic proportions would be expected if the genes for red eyes and for white-banded wings were located on different chromosomes?
- What is the percent recombination between the genes for red eyes and those for white-banded wings?
=> (SOLUTION)
3- A geneticist discovers a new mutation in Drosophila melanogaster that causes the flies to shake and quiver. She calls this mutation spastic (sps) and determines that spastic is due to an autosomal recessive gene. She wants to determine if the gene encoding spastic is linked to the recessive gene for vestigial wings (vg). She crosses a fly homozygous for spastic and vestigial traits with a fly homozygous for the wild-type traits and then uses the resulting F1 females in a testcross. She obtains the following flies from this testcross.
vg+ sps+ 230
vg sps 224
vg sps+ 97
vg+ sps 99
Total 650
Are the genes that cause vestigial wings and the spastic mutation linked? Do a chi-square test of independence to determine whether the genes have assorted independently.
=> (SOLUTION)
4- In cucumbers, heart-shaped leaves (hl) are recessive to normal leaves (Hi) and having numerous fruit spines (ns) is recessive to having few fruit spines (Ns). The genes for leaf shape and for number of spines are located on the same chromosome; findings from mapping experiments indicate that they are 32.6 m.u. apart. A cucumber plant having heart-shaped leaves and numerous spines is crossed with a plant that is homozygous for normal leaves and few spines. The F1, are crossed with plants that have heart-shaped Jeaves and numerous spines. What phenotypes and proportions are expected in the progeny of this cross?
=> (SOLUTION)
5- In tomatoes, tall (D) is dominant over dwarf (d) and smooth fruit (P) is dominant over pubescent fruit (p), which is covered with fine hairs. A farmer has two tall and smooth tomato plants, which we will call plant A and plant B. The farmer crosses plants A and B with the same dwarf and pubescent plant and obtains the following numbers of progeny:
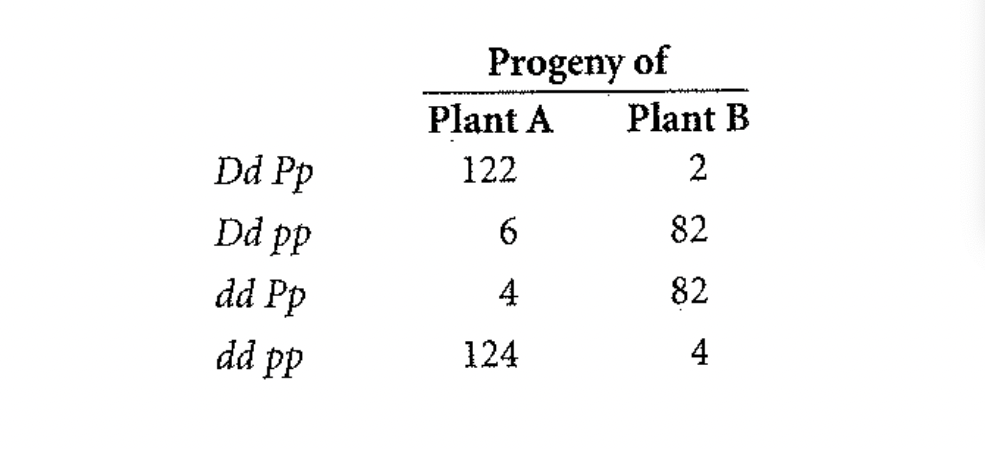
- What are the genotypes of plant A and plant B?
- Are the loci that determine height of the plant and pubescence linked? If so, what is the percent recombination between them?
- Explain why different proportions of progeny are produced when plant A and plant B are crossed with the same dwarf pubescent plant.
=> (SOLUTION)
6- Alleles A and a are at a locus on the same chromosome as is a locus with alleles B and b. Aa Bb is crossed with aa bb and the following progeny are produced:
Aa Bb 5
Aa bb 45
aa Bb 45
aa bb 5
What conclusion can be made about the arrangement of the genes on the chromosome in the Aa Bb parent?
=> (SOLUTION)
7- Daniel McDonald and Nancy Peer determined that eyespot (the clear spot in the center of the eye) in flour beetles is caused by an X-linked gene (es) that is recessive to the allele for the absence of eyespot (es+). They conducted a series of crosses to determine the distance between the gene for eyespot and the dominant X-linked gene for striped (St), which causes white stripes on females and acts as a recessive lethal (is lethal when homozygous in females or hemizygous and males). The following cross was carried out.

- Which progeny are the recombinants and which progeny are the non-recombinants?
- Calculate the recombination frequency between es and St.
- Are some potential genotypes missing among the progeny of the cross? If so, which ones and why?
=> (SOLUTION)
8- In German cockroaches, bulging eyes (bu) are recessive to normal eyes (bu+) And curved wings (cv) are recessive to straight wings (cv+). Both traits are encoded by autosomal genes that are linked. A cockroach has genotype bu+ bu cv+ cv, And the genes are in repulsion. Which of the following sets of genes will be found in the most common gametes produced by this cockroach?
- bu+ cv+
- bu cv
- bu+ bu
- cv+ cv
- bu cv+
Explain your answer.
=> (SOLUTION)
9- In Drosophila melanogaster, Ebony body (e) and rough eyes (ro) are encoded by autosomal recessive genes found on chromosome 3; they are separated by 20 m.u. The gene that encodes forked bristles (f) is X-linked recessive and assort independently of e and ro. Give the phenotypes of progeny and their expected proportions when a female of each of the following genotypes is test-crossed with a male.

=> (SOLUTION)
10- A series of two-point crosses were carried out among seven loci (a, b, c, d, e, f, and g), producing the following recombination frequencies. Map the seven loci, showing their linkage groups, the order of the loci in each linkage group, and the distances between the loci of each group.

=> (SOLUTION)
11- In snails,
D allele: coiling to the right (dextral)
d allele: coiling to the left (sinistral)
A parent snail in which the shell coils to the left (sinistral) undergoes self-fertilization, and all of the F1 progeny coil to the right.
- What is the genotype of the parent snail?
- If the F1 progeny are individually self-fertilized, what coiling phenotypes are expected?
The parental genotype: Dd
When F1 are individually self-fertilized, the DD and Dd will have rightward-coiled F2 progeny
(Dextral), and the dd individuals yield leftward coiled F2 progeny (sinistral).
The expected ratio is 3:1 dextral to sinistral
A snail (called Linpa) in which the shell coils to the right undergoes self-fertilization, and all of the F1 progeny coil to the left. A F1 male is crossed with a female (called Martha) from another population. The F2 population all coil right. When the F2 population is selfed individually, F3 shows 50% right coiling and 50% left coiling snails.
- What are the genotypes of Linpa’s parents?
- What is the genotype of Linpa?
- What is the genotype of Martha?
1- Limpa’s mom: Dd
Linpa’s dad: dd or Dd
2- Linpa: dd
3- Martha: Dd