Solved Problems
Part 4
1- Fur color in the rabbit, a furry little animal and popular pet, is determined by a pair of alleles, B and b. BB and Bb rabbits are black, and bb rabbits are white. A farmer wants to breed rabbits for sale. True-breeding white (bb) female babies breed poorly. The farmer purchases a pair of black rabbits, and these mate and produce six black and two white offspring. The farmer immediately sells his white rabbits, and then he comes to consult you for a breeding strategy to produce more white rabbits.
- If he performed random crosses between pairs of F1 black rabbits, what proportion of the F2 progeny would be white?
- If he crossed an F1 male to the parental female, what is the probability that this cross would produce white progeny?
- What would be the farmer’s best strategy to maximize the production of white rabbits?
=> (SOLUTION)
2- Genes a, b, and c assort independently and are recessive to their respective alleles A, B, and C. Two triply heterozygous (Aa Bb Cc) individuals are crossed.
- What is the probability that a given offspring will be phenotypically A B C—that is, will exhibit all three dominant traits?
- What is the probability that a given offspring will be homozygous for all three dominant alleles?
=> (SOLUTION)
3- Two homozygous strains of corn are hybridized. They are distinguished by six different pairs of genes, all of which assort independently and produce an independent phenotypic effect. The F1 hybrid is selfed to give an F2
- What is the number of possible genotypes in the F2 plants?
- How many of these genotypes will be homozygous at all six gene loci?
- If all gene pairs act in a dominant-recessive fashion, what proportion of the F2 plants will be homozygous for all dominants?
- What proportion of the F2 will show all dominant phenotypes?
=> (SOLUTION)
4- The coat color of mice is controlled by several genes. The agouti pattern, characterized by a yellow band of pigment near the tip of the hairs, is produced by the dominant allele A; homozygous aa mice do not have the band and are nonagouti. The dominant allele B determines black hairs, and the recessive allele b determines brown. Homozygous chch individuals allow pigments to be deposited only at the extremities (e.g., feet, nose, and ears) in a pattern called Himalayan. The genotype C– allows pigment to be distributed over the entire body.
- If a true-breeding black mouse is crossed with a true- breeding brown, agouti, Himalayan mouse, what will be the phenotypes of the F1 and F2 generation?
- What proportion of the non-Himalayan black agouti F2 animals will be Aa BB Cch?
- What proportion of the Himalayan mice in the F2 generation is expected to show brown pigment?
- What proportion of all agoutis in the F2 generation is expected to show black pigment?
=> (SOLUTION)
5- In cocker spaniels, solid coat color is dominant over spotted coat. Suppose a true-breeding, solid-colored dog is crossed with a spotted dog, and the F1 dogs are interbred.
- What is the probability that the first puppy born will have a spotted coat?
- What is the probability that, if four puppies are born, all of them will have solid coats?
=> (SOLUTION)
6- In the F2 of his cross of red-flowered x white-flowered Pisum (pea plant), Mendel obtained 705 plants with red flowers and 224 with white.
- Is this result consistent with his hypothesis of factor segregation, which predicts a 3:1 ratio?
- In how many similar experiments would a deviation
as great as or greater than this one be expected?
=> (SOLUTION)
7- In tomatoes, cut leaf and potato leaf are alternative characters, with cut (C) dominant to potato (c). Purple stem and green stem are another pair of alternative characters, with purple (P) dominant to green (p). A true- breeding cut, green tomato plant is crossed with a true-breeding potato, purple plant, and the F1 plants are allowed to interbreed. The 320 F2 plants were phenotypically 189 cut, purple; 67 cut, green; 50 potato, purple; and 14 potato, green. Propose a hypothesis to explain the data, and use the chi-square test to test the hypothesis.
=> (SOLUTION)
8- For the following pedigrees A and B, indicate whether the trait involved in each case could be recessive or dominant, and explain your answers:
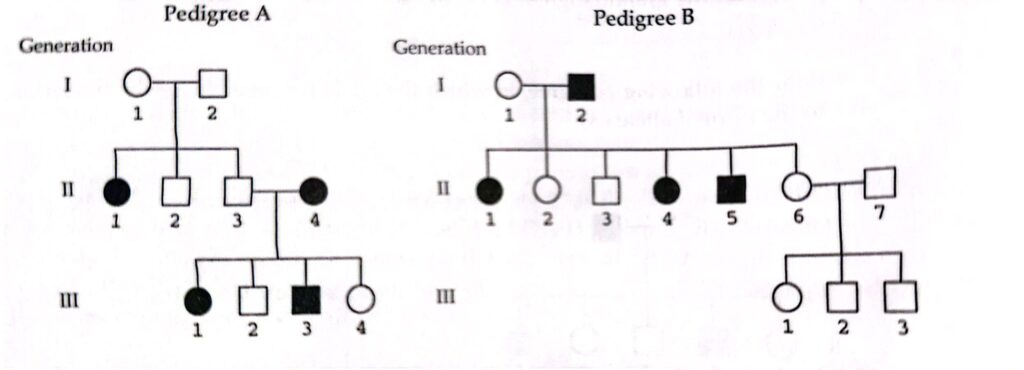
=> (SOLUTION)
9- After a few years of marriage, a woman comes to believe that, among all of the reasonable relatives in her and her husband’s families, her husband, her mother-in-law, and her father have so many similarities in their unreasonableness that they must share a mutation. A friend taking a course in genetics assures her that it is unlikely that this trait has a genetic basis and that, even if it did, all of her children would be reasonable. Diagram and analyze the relevant pedigree to evaluate whether the friend’s advice is accurate.
=> (SOLUTION)
10- Consider a diploid organism that has three pairs of chromosomes. Assume that the organism receives chromosomes A, B, and C from the female parent and A’, B’, and C’ from the male parent. Answer the following questions, assuming that crossing-over does not occur:
- What proportion of the gametes of this organism would be expected to contain all the chromosomes of maternal origin?
- What proportion of the gametes would be expected to contain some chromosomes of both maternal and paternal origin?
=> (SOLUTION)
11- At the time of synapsis preceding the reduction division in meiosis, the homologous chromosomes align in pairs, and one number of each pair passes to each of the daughter nuclei. In an animal with five pairs of chromosomes, assume that chromosomes 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 have come from the father, and 1′, 2′, 3′, 4′, and 5′ have come from the mother. Assuming no crossing-over, in what proportion of the gametes of this animal will all the paternal chromosomes be present together?
=> (SOLUTION)
12- In Drosophila, white eyes are a sex-linked character. The mutant allele for white eyes (w) is recessive to the wild-type allele for brick-red eye color (w+). A white-eyed female is crossed with a red-eyed male. An F1 female from this cross is mated with her father, and an F1 male is mated with his mother. What will be the eye color of the offspring of these last two crosses?
=> (SOLUTION)
13- In humans, red-green color blindness is recessive and X-linked, whereas albinism is recessive and autosomal. What types of children can be produced as the result of marriages between two homozygous parents; a normal-visioned albino woman and a color-blind, normally pigmented man?
=> (SOLUTION)
14- In Drosophila, vestigial (partially formed) wings (vg) are recessive to normal long wings (vg+), and the gene for this trait is autosomal. The gene for the white-eyed trait is on the X chromosome. Suppose a homozygous white-eyed, long-winged female fly is crossed with a homozygous red-eyed, vestigial-winged male.
- What will be the genotypes and phenotypes of the F1 flies?
- What will be the genotypes and phenotypes of the F2 flies?
=> (SOLUTION)
15- In Drosophila, two red-eyed, long-winged flies are bred together and produce the offspring listed in the following table:

=> (SOLUTION)
16- In chickens, a dominant sex-linked gene (B) produces barred feathers, and the recessive allele (b), when homozygous, produces nonbarred (solid-color) feathers. Suppose a non-barred cock is crossed with a barred hen.
- What will be the appearance of the F1 birds?
- If an F1 female is mated with her feather, what will be the appearance of the offspring?
- If an F1 male is mated with his mother, what will be the appearance of the offspring?
=> (SOLUTION)
17- A man (A) suffering from defective tooth enamel, which results in brown-colored teeth, marries a normal woman. All their daughters have brown teeth, but the sons are normal. The sons of man A marry normal women, and all their children are normal. The daughters of man A marry normal men, and 50 percent of their children have brown teeth. Explain these facts genetically.
=> (SOLUTION)
18- In humans, differences in the ability to taste phenylthiourea are due to a pair of autosomal alleles. Inability to taste is recessive to ability to taste. A child who is a nontaster is born to a couple who can both taste the substance. What is the probability that their next child will be a taster?
=> (SOLUTION)
19- Suppose gene A is on the X chromosome, and genes B, E, and D are on three different autosomes. Thus, A- signifies the dominant phenotype in the male or female. An equivalent situation holds for B-, E-, and D-. The cross is AA BB EE DD (female) X aY bb ee dd (male) is made.
- What is the probability of obtaining an A- individual in the F1 progeny?
- What is the probability of obtaining an a male in the F1 progeny?
- What is the probability of obtaining A- B- E- D- female in the F1 progeny?
- How many different F1 genotypes will there be?
- What proportion of F2 individuals will be heterozygous for the four genes?
- Determine the probabilities of obtaining each of the following types in the F2 individuals: (1) A- bb EE dd (female), (2) aY BB Ee Dd (male), (3) AY bb EE dd (male), (4) aa bb Ee Dd (female).
=> (SOLUTION)
20- In human genetics, pedigrees are used to analyze inheritance patterns. Females are represented by a circle, males by a square. The figure that follows presents three 2-generation family pedigrees for a trait in humans. Normal individuals are represented by unshaded symbols, people with the trait by shaded symbols. For each pedigree (A, B, and C), state (by answering ‘yes’ or ‘no’ in the appropriate blank space) whether transmission of the trait can be accounted for on the basis of each of the listed simple modes of inheritance:
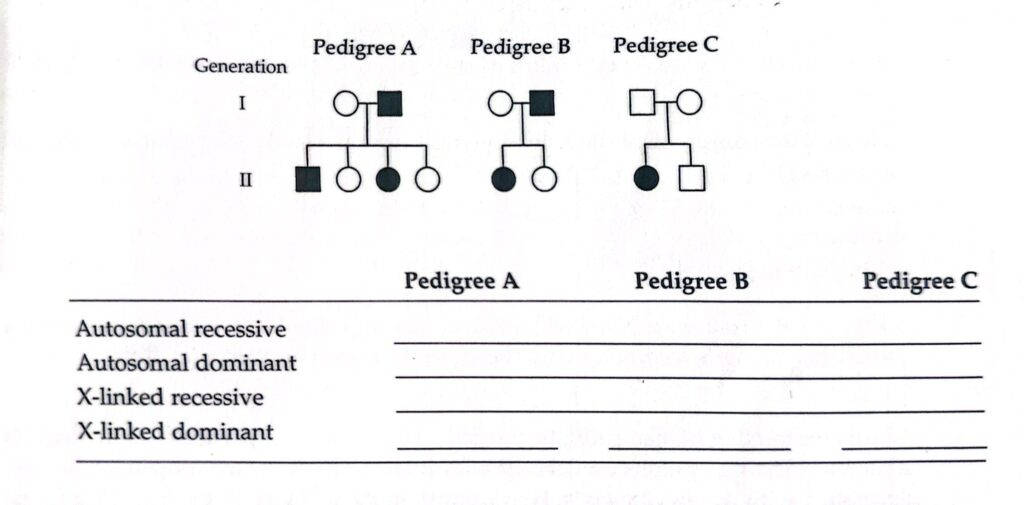
=> (SOLUTION)
21- Shaded symbols in the following pedigree represent a trait.
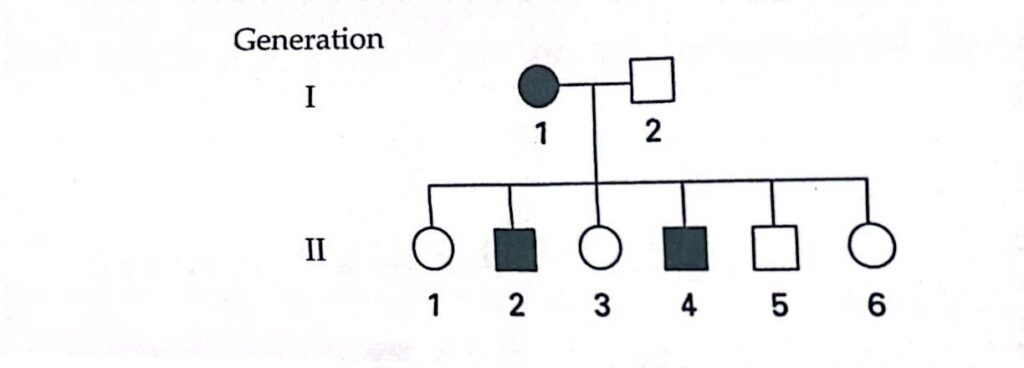
Which of the progeny eliminate X-linked recessiveness as a mode of inheritance for the trait?
- I-1 and I-2
- II-4
- II-5
- II-2 and II-4
=> (SOLUTION)
22- When constructing human pedigrees, geneticists often refer to particular individuals by a number. The generations are labeled with Roman numerals, the individuals in each generation with Arabic numerals. For example, in the pedigree in the following figure, the female with the asterisk is I-2:
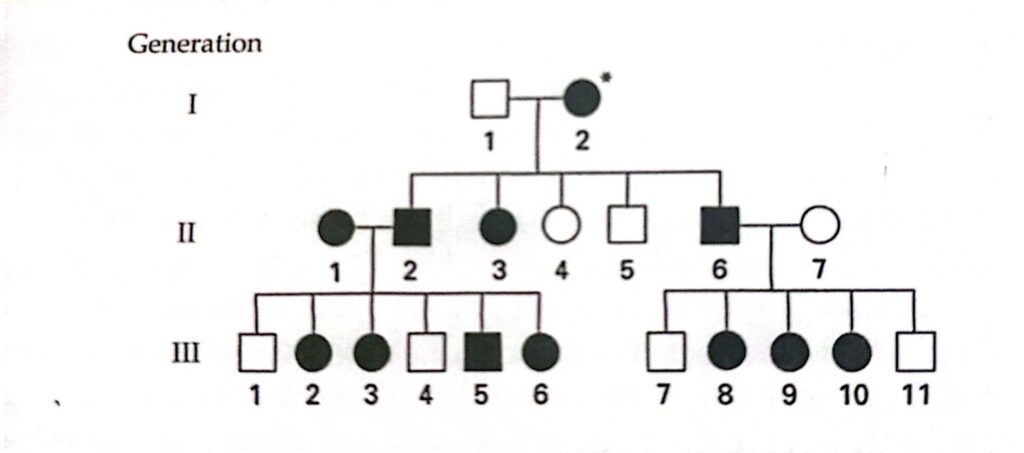
Use this means to designate specific individuals in the pedigree. Determine the probable inheritance mode for the trait shown in the affected individuals (the shaded symbols) by answering the following questions (assume that the condition is caused by a single gene):
- Y-linked inheritance can be excluded at a glance. What two other mechanisms of inheritance can be definitely excluded? Why can these be excluded?
- Of the remaining mechanisms of inheritance, which is the most likely? Why?
=> (SOLUTION)
23- Which of the following statements is not true for a disease that is inherited as a rare X-linked dominant trait?
- All daughters of an affected male will inherit the disease.
- Sons will inherit the disease only if their mothers have it.
- Both affected males and affected females will pass the trait to half the children.
- Daughters will inherit the disease only if their fathers have it.
=> (SOLUTION)
24- Albinism in humans is inherited as a simple recessive trait. For the following families, determine the genotypes of the parents and offspring. (When two alternative genotypes are possible, list both.)
- Two normal parents have five children, four normal and one albino.
- A normal male and an albino female have six children, all normal.
- A normal male and an albino female have six children, three normal and three albino.
- Construct a pedigree of the families in (b) and (c). Assume that one of the normal children in (b) and one of the albino children in (c) become the parents of eight children. Add these children to the pedigree, predicting their phenotypes (normal or albino).
=> (SOLUTION)
25- In Drosophila, gray body color is dominant to ebony body color, while long -wings are dominant to vestigial wings. Assuming that the P, individuals are homozygous, work the following crosses through the F2 generation, and determine the genotypic and phenotypic ratios for each generation.
- gray, long × ebony, vestigial
- gray, vestigial X ebony, long
- gray, long X gray, vestigial
=> (SOLUTION)
26- How many different types of gametes can be formed by individuals of the following genotypes: (a) AaBb, (b) AaBB, (c) AaBbCc, (d) AaBBcc, (e) AaBbcc, and (f) AaBbCcDdEe? What are the gametes in each case?
=> (SOLUTION)
27- In assessing data that fell into two phenotypic classes, a geneticist observed values of 250:150. She decided to perform a X2 analysis by using the following two different null hypotheses: (a) the data fit a 3:1 ratio, and (b) the data fit a 1:1 ratio. Calculate the X2 values for each hypothesis. What can be concluded about each hypothesis?
=> (SOLUTION)
28- The basis for rejecting any null hypothesis is arbitrary. The researcher can set more or less stringent standards by deciding to raise or lower the p value used to reject or not reject the hypothesis. In the case of the chi-square analysis of genetic crosses, would the use of a standard of p = 0.10 be more or less stringent about not rejecting the null hypothesis? Explain.
=> (SOLUTION)
29- In a family of five children, what is the probability that
- all are males?
- three are males and two are females?
- two are males and three are females?
- all are the same sex?
Assume that the probability of a male child is equal to the probability of a female child (p = 1/2).
=> (SOLUTION)
30- In a family of eight children, where both parents are heterozygous for albinism, what mathematical expression predicts the probability that six are normal and two are albinos?
=> (SOLUTION)
31- A “wrongful birth” case was recently brought before a court in which a child with Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome was born to apparently healthy parents. This syndrome is characterized by a cluster of birth defects including cleft palate, and an array of problems with the reproductive and urinary organs. Originally considered by their physician as having a nongenetic basis, the parents decided to have another child, who was also born with Smith-Lemli-Opitz syndrome. In the role of a genetic counselor, instruct the court about what occurred, including the probability of the parents having two affected offspring, knowing that the disorder is inherited as a recessive trait.
=> (SOLUTION)
32- Two true-breeding pea plants were crossed. One parent is round, terminal, violet, constricted, while the other expresses the respective contrasting phenotypes of wrinkled, axial, white, full. The four pairs of contrasting traits are controlled by four genes, each located on a separate chromosome. In the F1 only round, axial, violet, and full were expressed. In the F2, all possible combinations of these traits were expressed in ratios consistent with Mendelian inheritance.
- What conclusion about the inheritance of the traits can be drawn based on the F1 results?
- In the F2 results, which phenotype appeared most frequently? Write a mathematical expression that predicts the probability of occurrence of this phenotype.
- Which F2 phenotype is expected to occur least frequently? Write a mathematical expression that predicts this probability.
=> (SOLUTION)
33- To assess Mendel’s law of segregation using tomatoes, a true-breeding tall variety (SS) is crossed with a true-breeding short variety (ss). The heterozygous F1, tall plants (Ss) were crossed to produce two sets of F2 data, as follows.
Set I: 30 tall, 5 short
Set II: 300 tall, 50 short
- Using the X2 test, analyze the results for both datasets. Calculate X2 values and estimate the p values in both cases.
- From the above analysis, what can you conclude about the importance of generating large datasets in experimental conditions?
=> (SOLUTION)
34- Alkaptonuria is a metabolic disorder in which affected persons produce black urine. Alkaptonuria results from an allele (a) that is recessive to the allele for normal metabolism (A). Sally has normal metabolism, but her brother has alkaptonuria. Sally’s father has alkaptonuria, and her mother has normal metabolism.
- Give the genotypes of Sally, her mother, her father, and her brother.
- If Sally’s parents have another child, what is the probability that this child will have alkaptonuria
- If Sally marries a man with alkaptonuria, what is the probability that their first child will have alkaptonuria?
=> (SOLUTION)
35- What is the probability of rolling one six-sided die and obtaining the following numbers?
- 2
- 1 or 2
- An even number
- Any number but a 6
=> (SOLUTION)
36- What is the probability of rolling two six-sided dice and obtaining the following numbers?
- 2 and 3
- 6 and 6
- At least one 6
- Two of the same number (two 1s, or two 2s, or two 3s, etc.)
- An even number on both dice
- An even number on at least one die
=> (SOLUTION)
37- In a family of seven children, what is the probability of obtaining the following numbers of boys and girls?
- All boys
- All children of the same sex
- Six girls and one boy
- Four boys and three girls
=> (SOLUTION)
38- Phenylketonuria (PKU) is a disease that results from a recessive gene. Two normal parents produce a child with PKU.
- What is the probability that the sperm from the father will contain the PKU allele?
- What is the probability that an egg from the mother will contain the PKU allele?
- What is the probability that their next child will have PKU?
- What is the probability that their next child will be heterozygous for the PKU gene?
=> (SOLUTION)
39- The following two genotypes are crossed:
Aa Bb Cc dd Ee X Aa bb Cc Dd Ee.
What will the proportion of the following genotypes be among the progeny of this cross?
- Aa Bb Cc Dd Ee
- Aa bb Cc dd ee
- aa bb cc dd ee
- AA BB CC DD EE
=> (SOLUTION)
40- In mice, an allele for apricot eyes (a) is recessive to an allele for brown eyes (a+). At an independently assorting locus, an allele for tan coat color (t) is recessive to an allele for black coat color (t+). A mouse that is homozygous for brown eyes and black coat color is crossed with a mouse having apricot eyes and a tan coat. The resulting F1 is crossed to produce the F2. In a litter of eight F2 mice, what is the probability that two will have apricot eyes and tan coats?
=> (SOLUTION)
41- A Moore investigated the inheritance of spotting patterns in leopard frogs (J.A. Moore. 1943. Journal of Heredity 34:3-7). The pipiens phenotype had the normal spots that give leopard frogs their name. In contrast, the burnsi phenotype lacked spots on its back. Moore carried out the following crosses, producing the progeny indicated.
Parent phenotypes | Progeny phenotypes |
burnsi X burnsi | 39 burnsi, 6 pipiens |
burnsi X pipiens | 23 burnsi, 33 pipiens |
burnsi X pipiens | 196 burnsi, 210 pipiens |
- On the basis of these results, what is the most likely mode of inheritance of the burnsi phenotype?
- Give the most likely genotypes of the parent in each cross (use B for the burnsi allele and B+ for pipiens allele)
- Use a chi-square test to evaluate the fit of the observed numbers of progeny to the number expected on the basis of your proposed genotypes.
=> (SOLUTION)