Solved Problems
Part 4
1- Heterozygous Dd chickens express a condition called creeper, in which the leg and wing bones are shorter than normal (dd). The dominant D allele is lethal when homozygous. Two alleles of an independently segregating gene determine white (B—) versus yellow (bb) skin color. From matings between chickens heterozygous for both of these genes, what phenotypic classes will be represented among the viable progeny, and what are their expected relative frequencies?
Because the genes segregate independently, they can be considered separately. For the D, d pair of alleles, the genotypes of the zygotes are DD, Dd, and dd in the proportions 1/4, 1/2, and 1/4, respectively. However, the DD zygotes do not survive, so among the survivors, the genotypes are Dd (creeper) and dd (noncreeper), in the proportions 2/3 and 1/3, respectively. For the B, b pair of alleles, the progeny genotypes are B- (white) and bb (yellow), in the proportions 3/4 and 1/4, respectively. Altogether, the phenotypes and proportions of the surviving offspring can be obtained by multiplying (2/3 creeper + 1/3 noncreeper) × (3/4 white + 1/4 yellow), which yields 6/12 creeper, white + 2/12 creeper, yellow + 3/12 noncreeper, white + 1/12 noncreeper, yellow. Note that the proportions sum to 12/12 = 1, which serves as a check.
2- White Leghorn chickens are homozygous for a dominant allele, D, of a gene responsible for colored feathers, and also for a dominant allele, I, of an independently segregating gene that prevents the expression of D. The White Wyandotte breed is homozygous recessive for both genes dd ii. What proportion of the F2 progeny obtained from mating White Leghorn × White Wyandotte F1 hybrids would be expected to have colored feathers?
Colored offspring must have the genotype D- ii; otherwise, color could not be produced (as in dd) or would be suppressed (as in I-). Among the F2 progeny, 3/4 of the offspring have the D- genotype, and 1/4 of the offspring have the ii genotype. Because the genes undergo independent assortment, the overall expected proportion of colored offspring is (3/4) × (1/4) = 3/16.
3- The F2 progeny from a particular cross exhibit a modified dihybrid ratio of 9:7 (instead of 9:3:3:1). What phenotypic ratio would be expected from a testcross of the F1?
The 9:3:3:1 ratio is that of the genotypes A- B-, A- bb, aa B-, and aa bb. The modified 9:7 ratio implies that all of the last three genotypes have the same phenotype. The F1 testcross is between the genotypes Aa Bb × aa bb, and the progeny are expected in the proportions 1/4 Aa Bb, 1/4 Aa bb, 1/4 aa Bb, and 1/4 aa bb. Again, the last three genotypes have the same phenotype, so the ratio of phenotypes among progeny of the testcross is 1:3.
4- Andalusian fowls are colored black, splashed white (resulting from an uneven sprinkling of black pigment through the feathers), or slate blue. Black and splashed white are true breeding, and slate blue is a hybrid that segregates in the ratio 1 black : 2 slate blue : 1 splashed white. If a pair of blue Andalusians is mated and the hen lays three eggs, what is the probability that the chicks hatched from these eggs will be one black, one blue, and one splashed white?
Black and splashed white are the homozygous genotypes and slate blue the heterozygote. The probabilities of each of these phenotypes from the mating between two heterozygotes are 1/4 black, 1/2 slate blue, and 1/4 splashed white. The probability of occurrence of the particular birth order black, slate blue, and splashed white is (1/4) × (1/2) × (1/4) = 1/32, but altogether there are six different orders in which exactly one of each type could be produced. (The black offspring could be first, second, or third, and in each case, the remaining phenotypes could occur in either of two orders.) Consequently, the overall probability of one of each phenotype, in any order, is 6 × (1/32) = 3/16
5- You are provided with the following pedigree:

The mode of inheritance of this trait is:
a) Sex-limited
b) Sex-influenced dominant in the female but recessive in the male
c) Sex-influenced recessive in the female but dominant in the male
d) Sex-linked
Answer: b
1)AA, 2)aa, 3)AA, 4)Aa, 5)Aa, 6)Aa, 7)Aa, 8)aa, 9)AA, 10)A_, 11)Aa, 12)Aa, 13)_a, 14)aa
6- You are provided with the following pedigree:
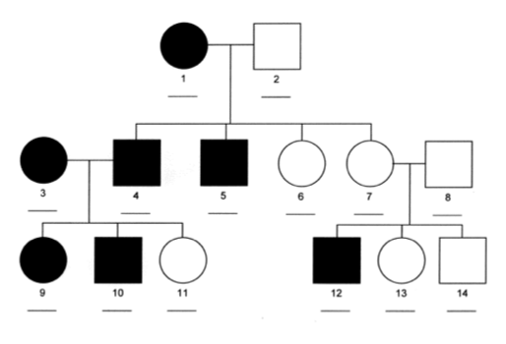
The mode of inheritance of this trait is:
a) Sex-limited
b) Sex-influenced dominant in the female but recessive in the male
c) Sex-influenced recessive in the female but dominant in the male
d) Sex-linked
Answer: c
1)AA, 2)aa, 3)AA, 4)Aa, 5)Aa, 6)Aa, 7)Aa, 8)aa, 9)AA, 10)A_, 11)Aa, 12)Aa, 13)Aa, 14)aa
7- True-breeding orchids can have white and red flowers. The hybrids between these two have pink flowers. The red color has 70% penetrance with 30% of the time the same henotype showing white color.
When two pink orchids are crossed, what percentage of the F1 generation will be white?
0.25 (Red genotype) x 0.7 (penetrance) = 0.175
Therefore, out of the 25% of the plant with the red genotype only 17.5% will be red. The remaining 7.5% will be white.
Therefore the total percentage of white flowers in the F1 generation will be: 25% + 7.5% = 32.5%.